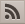Authentication
GET-requests for private UNITs and any PUT-, POST-, DELETE-request must use the HTTP-Basic-Authentication-Header to specify username (email-address) and password.
Only the owner of a UNIT is authorized to make PUT-, POST-, DELETE-requests, whereas other users - even registered with other providers - can also be authorized to make requests for private UNITs.
Example: Alice (alice@provider_a.com) was authorized from Bob (bob@provider_b.com) to request a private UNIT (by adding her email-address to the list of authorized follower). Alice is registered at UP_PROVIDER_A (www.a-provider.com) whereas Bob at UP_PROVIDER_B (www.b-provider.com). The problem: Alice has to authenticate with her email-address and a password, but UP_PROVIDER_B doesn't even know Alice!!!
If a user wants to access a provider where he is not registered, a password can be requested beforehand. Since this request itself cannot be authenticated, the password is encrypted with the requesting user's public key.
The following two UNITs are used for this purpose.
1) PKY
| Variable | Description | Example |
privatekey |
Private Key in PEM format |
----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY---- |
publickey |
Public Key in PEM format |
----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY---- |
e_hash |
SHA-512 |
|
n_keybits |
4096 | 2048 (integer) |
4096 |
e_algorithm |
RSA |
RSA |
2) PWD - Password
The pwd-UNIT is a special UNIT. It is called without AuthenticationHeader usually from a UP_USER that is not registered at the requested UP_PROVIDER.
| Variable | Description | Example |
_cpwd |
password encrpted with the PublicKey of the requesting user |
Mjdx5djleoc12?.... |